New biocomputing method uses enzymes as catalysts for DNA-based molecular computing UMNews NatureComms
A typical NOT gate reaction consists of 1 μL of a restriction enzyme, 3 μL of 5X aHOT 7.9 buffer, 1 μL of 25 μM gate template, 1 μL of 25 μM T7 Max promoter sense complement, 3 μL of 25 μM input when applicable, and ddHO to bring the volume up to 15 μl. Reaction A was subjected to the same annealing and digest incubation protocols mentioned above.
The AND gate Reaction A utilizes New England Biolabs OneTaq Polymerase PCR recommendations. However, instead of running the reaction for 30 cycles, the AND gate only requires one cycle. Each AND gate reaction has a final volume of 25μL and includes 5μL of OneTaq 5X Standard Reaction Buffer , 1 μL of 100 μM Input 1, 1 μL of 100 μM Input 2, 0.
All gate Reaction As were used as the template for a cell-free transcription reaction that produces a fluorescent RNA aptamer. This transcription reaction will be referred to as Reaction B in this Methods. Typical cell-free transcription reactions are quite compact in volume , but because Reaction A volumes were a minimum of 7 μL and often contained highly concentrated gate templates, the concentration of reagents were increased to compensate.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
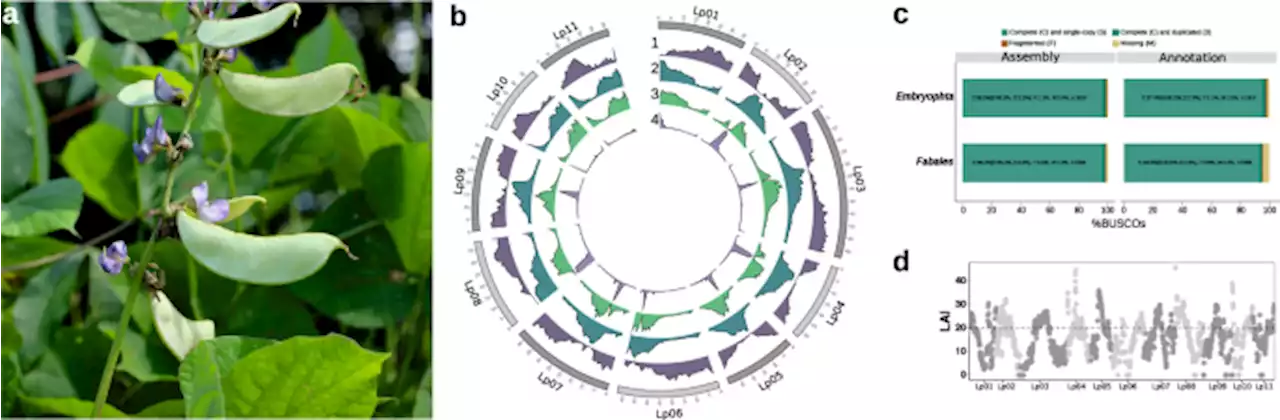 Chromosome-level genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate orphan crop lablab breeding - Nature CommunicationsLablab is a legume native to Africa and cultivated throughout the tropics for food and forage; however, as an orphan crop, limited genomic resources hampers its genetic improvement. Here, an African-led South-North plant genome collaboration produces an improved genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate its breeding.
Chromosome-level genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate orphan crop lablab breeding - Nature CommunicationsLablab is a legume native to Africa and cultivated throughout the tropics for food and forage; however, as an orphan crop, limited genomic resources hampers its genetic improvement. Here, an African-led South-North plant genome collaboration produces an improved genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate its breeding.
Read more »
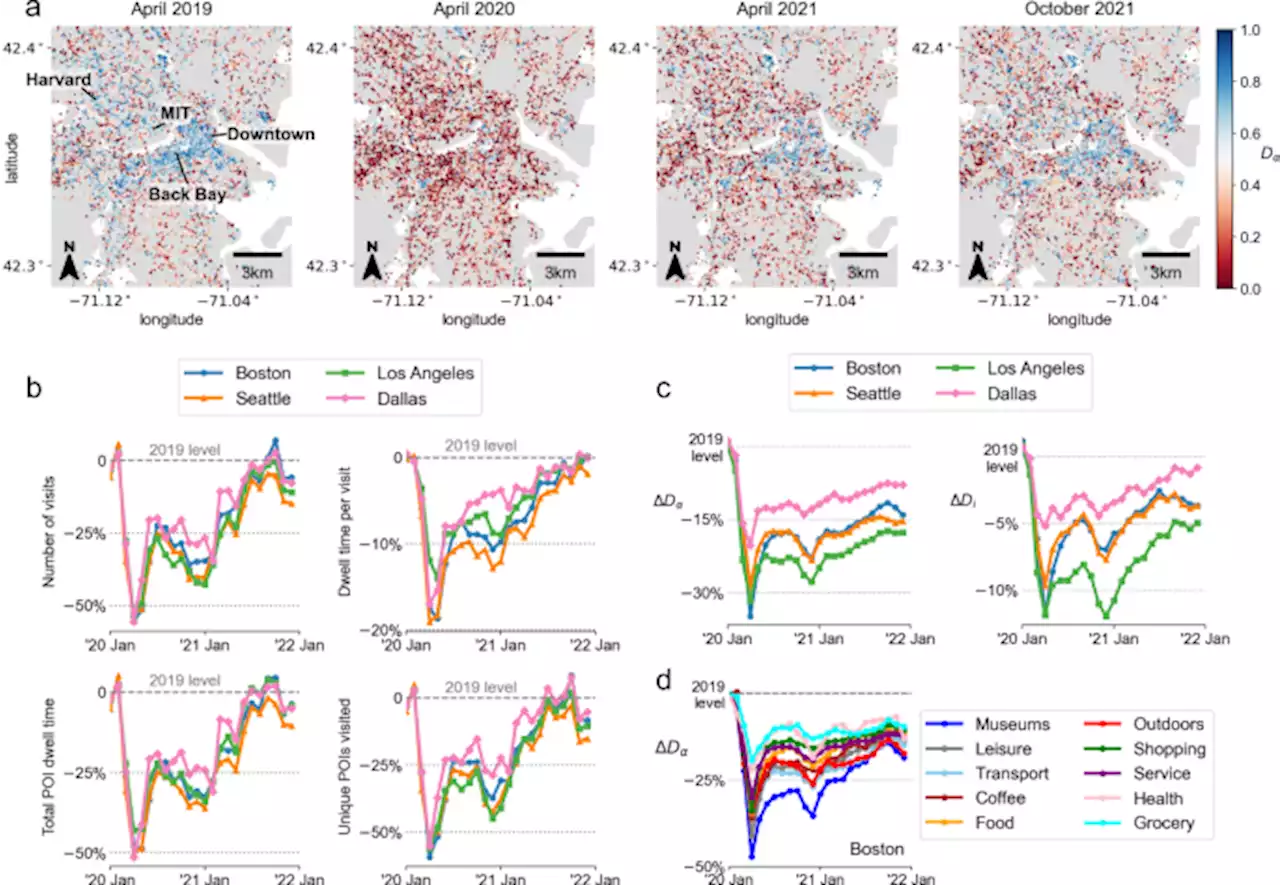 Behavioral changes during the COVID-19 pandemic decreased income diversity of urban encounters - Nature CommunicationsMobile phone data reveals a significant decrease in the income diversity of urban encounters during the COVID-19 pandemic in the USA, even though overall mobility returned to pre-pandemic levels by late 2021. This was mainly due to persistent behavioral changes including less willingness to explore new places.
Behavioral changes during the COVID-19 pandemic decreased income diversity of urban encounters - Nature CommunicationsMobile phone data reveals a significant decrease in the income diversity of urban encounters during the COVID-19 pandemic in the USA, even though overall mobility returned to pre-pandemic levels by late 2021. This was mainly due to persistent behavioral changes including less willingness to explore new places.
Read more »
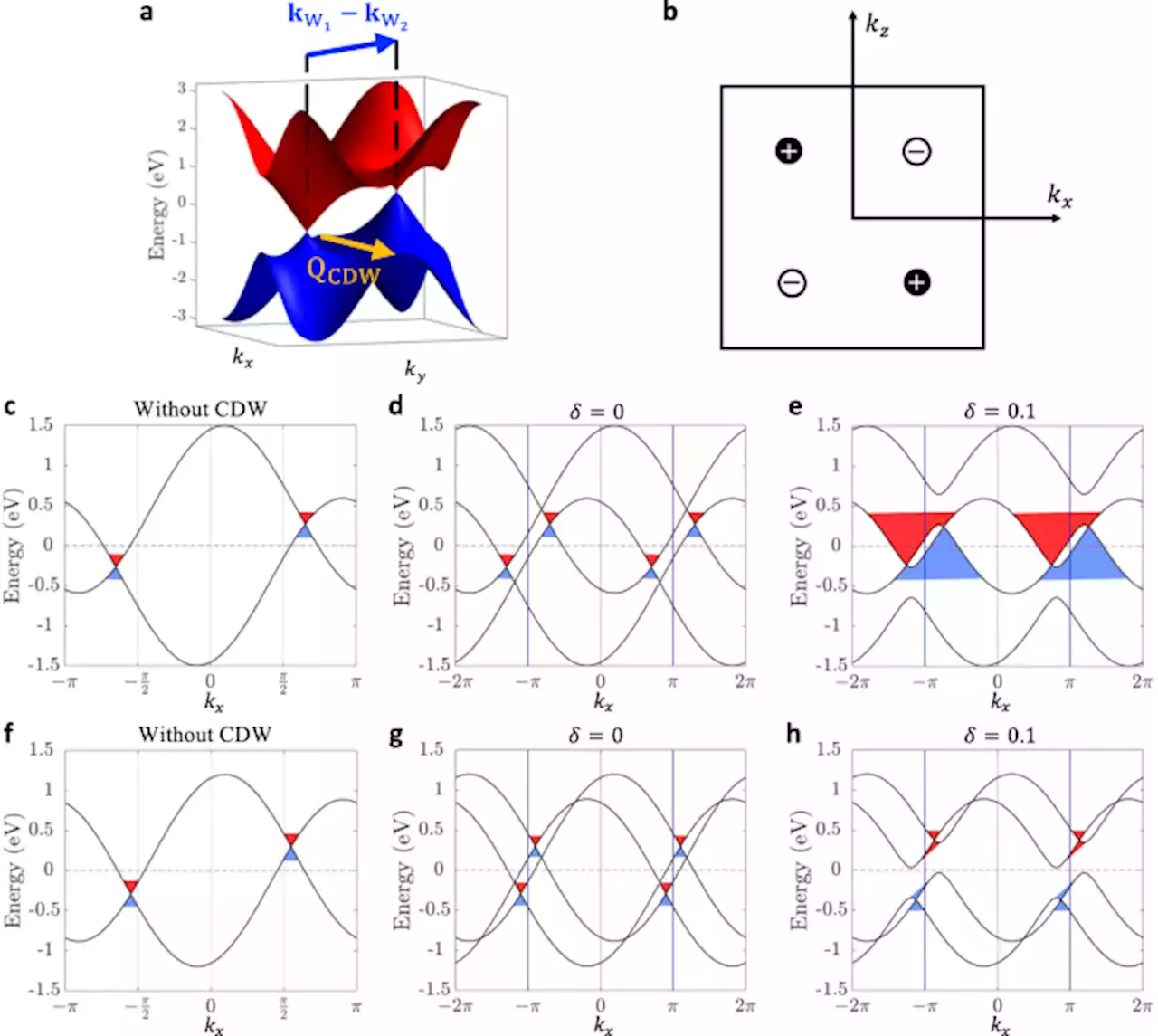 Causal structure of interacting Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems - Nature CommunicationsCausality, the relationship between cause and effect, is a central concept in Einstein’s theory of relativity. Here, authors show that a causality analogue in energy-momentum space plays an important role in describing quasiparticle interactions in quantum matter.
Causal structure of interacting Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems - Nature CommunicationsCausality, the relationship between cause and effect, is a central concept in Einstein’s theory of relativity. Here, authors show that a causality analogue in energy-momentum space plays an important role in describing quasiparticle interactions in quantum matter.
Read more »
 China Balks at U.S. Push for Better Communications During CrisesThe U.S. and China are struggling to develop reliable systems to communicate in a crisis, raising the risk that a miscalculation by either side’s military could spill into conflict
China Balks at U.S. Push for Better Communications During CrisesThe U.S. and China are struggling to develop reliable systems to communicate in a crisis, raising the risk that a miscalculation by either side’s military could spill into conflict
Read more »
 Comparative study of adaptive variational quantum eigensolvers for multi-orbital impurity models - Communications PhysicsQuantum embedding approaches to simulate condensed matter on quantum computers have been proposed, yet applications are limited to simplest models. The authors perform a systematic study of ground state preparation with variational quantum algorithms for correlated multi-orbital impurity models, addressing key issues toward real materials simulations.
Comparative study of adaptive variational quantum eigensolvers for multi-orbital impurity models - Communications PhysicsQuantum embedding approaches to simulate condensed matter on quantum computers have been proposed, yet applications are limited to simplest models. The authors perform a systematic study of ground state preparation with variational quantum algorithms for correlated multi-orbital impurity models, addressing key issues toward real materials simulations.
Read more »
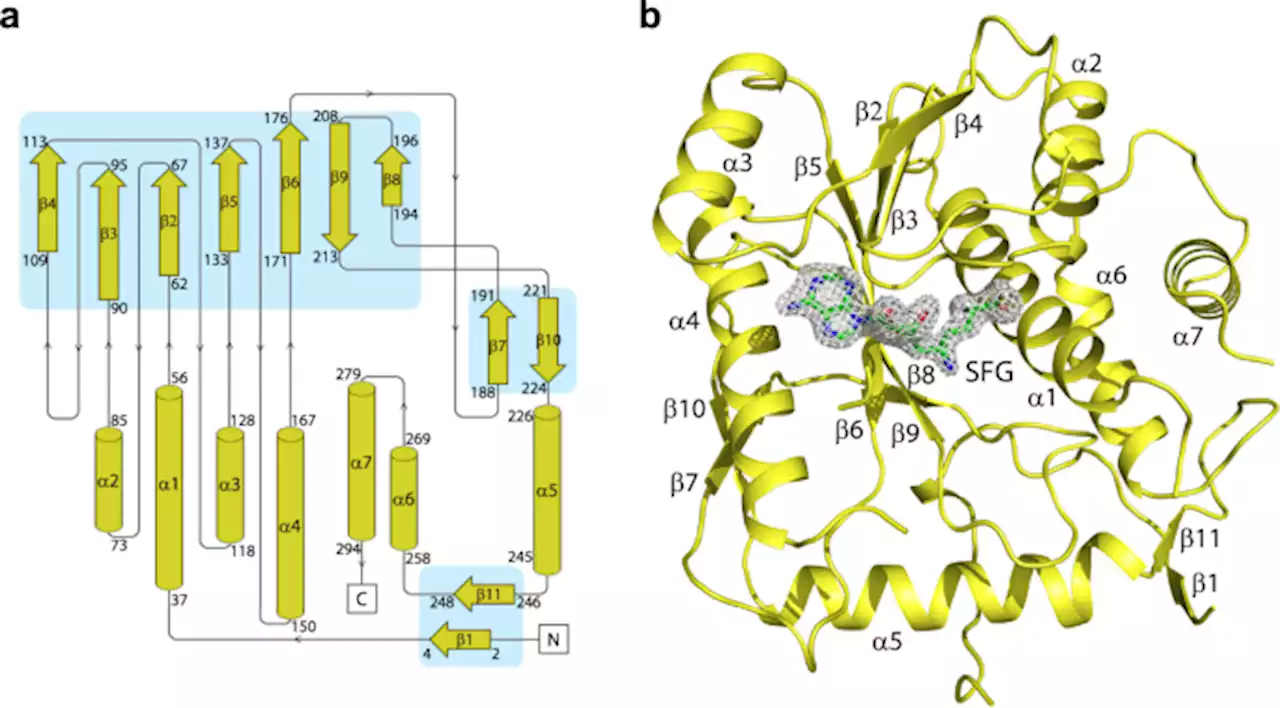 Discovery and structural characterization of monkeypox virus methyltransferase VP39 inhibitors reveal similarities to SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 methyltransferase - Nature CommunicationsMonkeypox virus is a pathogen with pandemic potential, encoding for its own RNA capping machinery. Here, the authors present crystal structures of its 2′-O-RNA methyltransferase VP39 in complex with sub-micromolar inhibitors and reveal similarities to SARS-CoV−2 nsp14 methyltransferase.
Discovery and structural characterization of monkeypox virus methyltransferase VP39 inhibitors reveal similarities to SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 methyltransferase - Nature CommunicationsMonkeypox virus is a pathogen with pandemic potential, encoding for its own RNA capping machinery. Here, the authors present crystal structures of its 2′-O-RNA methyltransferase VP39 in complex with sub-micromolar inhibitors and reveal similarities to SARS-CoV−2 nsp14 methyltransferase.
Read more »
