A team of researchers has successfully modified a naturally occurring chemical compound in the lab, resulting in advanced lead compounds with anti-HIV activity.
Researchers open new leads in anti-HIV drug development, using a compound found in nature." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 8 March 2024. <www.sciencedaily.comUniversity of Michigan. . Researchers open new leads in anti-HIV drug development, using a compound found in nature.
Scientists appear to have discovered a way to produce a true structure of the rare but naturally-occurring anti-HIV compound Lancilactone C from start to finish. The domino-like reaction enables the ... Researchers have successfully bulk-produced fat tissue in the lab that has a similar texture and make-up to naturally occurring fats from ...
When modified using a process known as epoxidation, two naturally occurring lipids are converted into potent agents that target multiple cannabinoid receptors in neurons, interrupting pathways that ...
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 After decades of failures, researchers have renewed hopes for an effective HIV vaccineBenjamin Ryan is independent journalist specializing in science and LGBTQ coverage. He contributes to NBC News, The New York Times, The Guardian and Thomson Reuters Foundation and has also written for The Washington Post, The Nation, The Atlantic and New York.
After decades of failures, researchers have renewed hopes for an effective HIV vaccineBenjamin Ryan is independent journalist specializing in science and LGBTQ coverage. He contributes to NBC News, The New York Times, The Guardian and Thomson Reuters Foundation and has also written for The Washington Post, The Nation, The Atlantic and New York.
Read more »
 Gender bias leads to lower-rated female films, researchers say'Barbie' might have won the dance-off against 'Oppenheimer' at the box office, but a new Robert H. Smith School of Business study may explain why the hot-pink bubble burst well before this Oscar weekend.
Gender bias leads to lower-rated female films, researchers say'Barbie' might have won the dance-off against 'Oppenheimer' at the box office, but a new Robert H. Smith School of Business study may explain why the hot-pink bubble burst well before this Oscar weekend.
Read more »
 Researchers leverage machine learning to find surprising temperature-genome correlationA recent study by researchers uncover clues in extremophiles' genomes, revealing genomic shifts and hinting at astrobiological implications.
Researchers leverage machine learning to find surprising temperature-genome correlationA recent study by researchers uncover clues in extremophiles' genomes, revealing genomic shifts and hinting at astrobiological implications.
Read more »
 ChatGPT Is More Likely to Sentence People Who Speak African American English to Death, Researchers SayA new paper finds that while popular AI models may not be outwardly racist, they are covertly racist when it comes to African American English.
ChatGPT Is More Likely to Sentence People Who Speak African American English to Death, Researchers SayA new paper finds that while popular AI models may not be outwardly racist, they are covertly racist when it comes to African American English.
Read more »
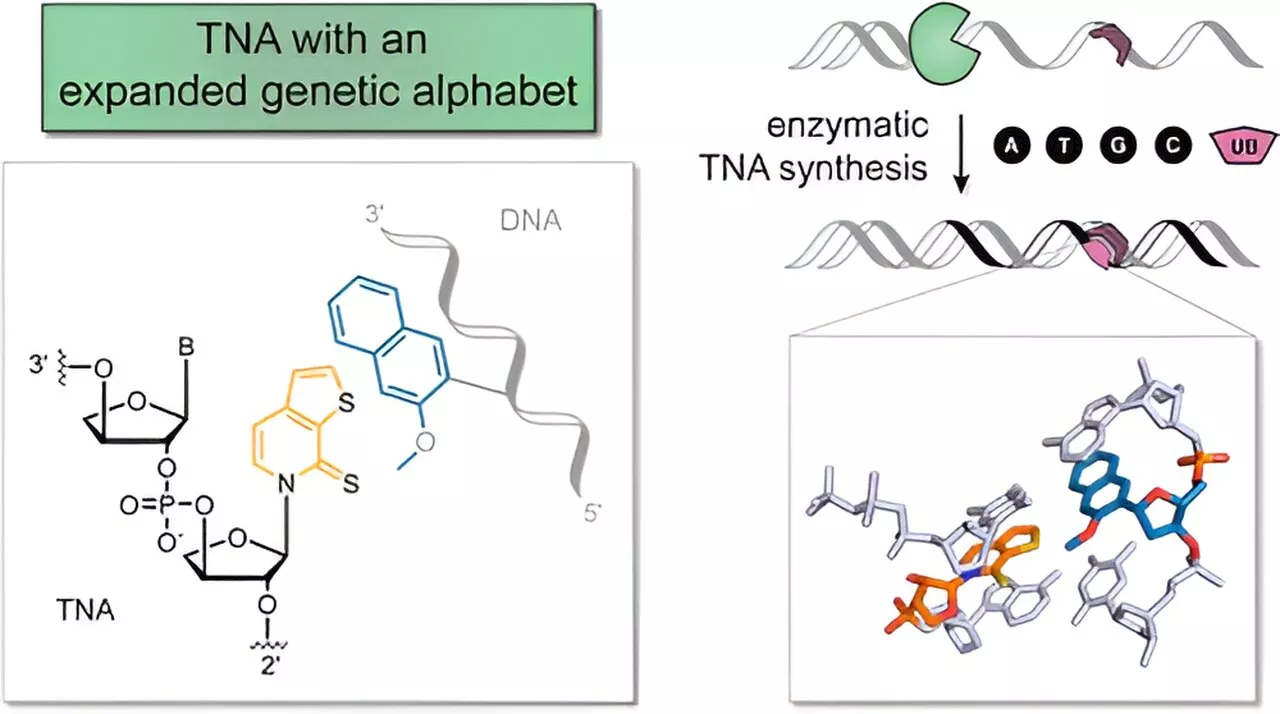 Researchers develop artificial building blocks of lifeFor the first time, scientists from the University of Cologne (UoC) have developed artificial nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, with several additional properties in the laboratory, which could be used as artificial nucleic acids for therapeutic applications.
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of lifeFor the first time, scientists from the University of Cologne (UoC) have developed artificial nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, with several additional properties in the laboratory, which could be used as artificial nucleic acids for therapeutic applications.
Read more »
 Researchers develop artificial building blocks of lifeFor the first time, scientists have developed artificial nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, with several additional properties in the laboratory.
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of lifeFor the first time, scientists have developed artificial nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, with several additional properties in the laboratory.
Read more »
