Data assimilation is an important mathematical discipline in earth sciences, particularly in numerical weather prediction (NWP). However, conventional data assimilation methods require significant computational resources.
Data assimilation is an important mathematical discipline in earth sciences, particularly in numerical weather prediction . However, conventional data assimilation methods require significant computational resources. To address this, researchers developed a novel method to solve data assimilation on quantum computers , significantly reducing the computation time.
In a recent study, Professor Shunji Kotsuki from the Institute for Advanced Academic Research/Center for Environmental Remote Sensing/Research Institute of Disaster Medicine, Chiba University, along with his colleagues Fumitoshi Kawasaki from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering and Masanao Ohashi from the Center for Environmental Remote Sensing, developed a novel data assimilation technique designed for quantum annealing machines.
The results revealed that quantum annealers produced analysis with comparable accuracy to conventional quasi-Newton-based approaches but in a fraction of the time they took. The D-Wave's Phy-QA required less than 0.05 seconds for computation, much faster than conventional approaches. However, it also exhibited slightly larger root mean square errors, which the researchers attributed to the inherent stochastic quantum effects.
Physics Quantum Computing Weather Severe Weather Floods Quantum Computers Computers And Internet Computer Modeling
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Quantum internet breakthrough after 'quantum data' transmitted through standard fiber optic cable for 1st timeDrew is a freelance science and technology journalist with 20 years of experience. After growing up knowing he wanted to change the world, he realized it was easier to write about other people changing it instead.
Quantum internet breakthrough after 'quantum data' transmitted through standard fiber optic cable for 1st timeDrew is a freelance science and technology journalist with 20 years of experience. After growing up knowing he wanted to change the world, he realized it was easier to write about other people changing it instead.
Read more »
 Pseudomagic quantum states: A path to quantum supremacyA new study in Physical Review Letters (PRL) introduces the concept of pseudomagic quantum states, which appear to have high stabilizerness (or complexity) and can move us closer to achieving quantum supremacy.
Pseudomagic quantum states: A path to quantum supremacyA new study in Physical Review Letters (PRL) introduces the concept of pseudomagic quantum states, which appear to have high stabilizerness (or complexity) and can move us closer to achieving quantum supremacy.
Read more »
 Toward testing the quantum behavior of gravity: A photonic quantum simulationIn a development at the intersection of quantum mechanics and general relativity, researchers have made significant strides toward unraveling the mysteries of quantum gravity.
Toward testing the quantum behavior of gravity: A photonic quantum simulationIn a development at the intersection of quantum mechanics and general relativity, researchers have made significant strides toward unraveling the mysteries of quantum gravity.
Read more »
 Groundbreaking progress in quantum physics: How quantum field theories decay and fissionAn international research team has sparked interest in the scientific community with results in quantum physics. In their current study, the researchers reinterpret the Higgs mechanism, which gives elementary particles mass and triggers phase transitions, using the concept of 'magnetic quivers.
Groundbreaking progress in quantum physics: How quantum field theories decay and fissionAn international research team has sparked interest in the scientific community with results in quantum physics. In their current study, the researchers reinterpret the Higgs mechanism, which gives elementary particles mass and triggers phase transitions, using the concept of 'magnetic quivers.
Read more »
 Theoretical quantum speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithmResearchers demonstrated a quantum algorithmic speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithm, laying the groundwork for advancements in telecommunications, financial modeling, materials science and more.
Theoretical quantum speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithmResearchers demonstrated a quantum algorithmic speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithm, laying the groundwork for advancements in telecommunications, financial modeling, materials science and more.
Read more »
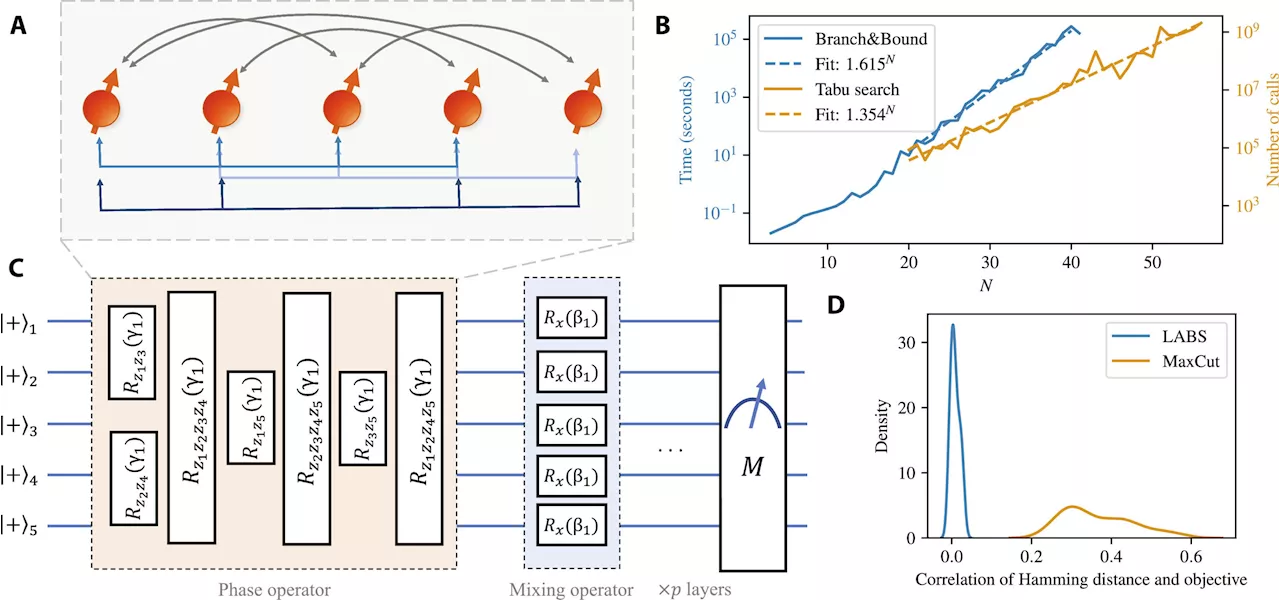 Research team shows theoretical quantum speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithmIn a new paper in Science Advances, researchers at JPMorgan Chase, the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Quantinuum have demonstrated clear evidence of a quantum algorithmic speedup for the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA).
Research team shows theoretical quantum speedup with the quantum approximate optimization algorithmIn a new paper in Science Advances, researchers at JPMorgan Chase, the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Quantinuum have demonstrated clear evidence of a quantum algorithmic speedup for the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA).
Read more »
