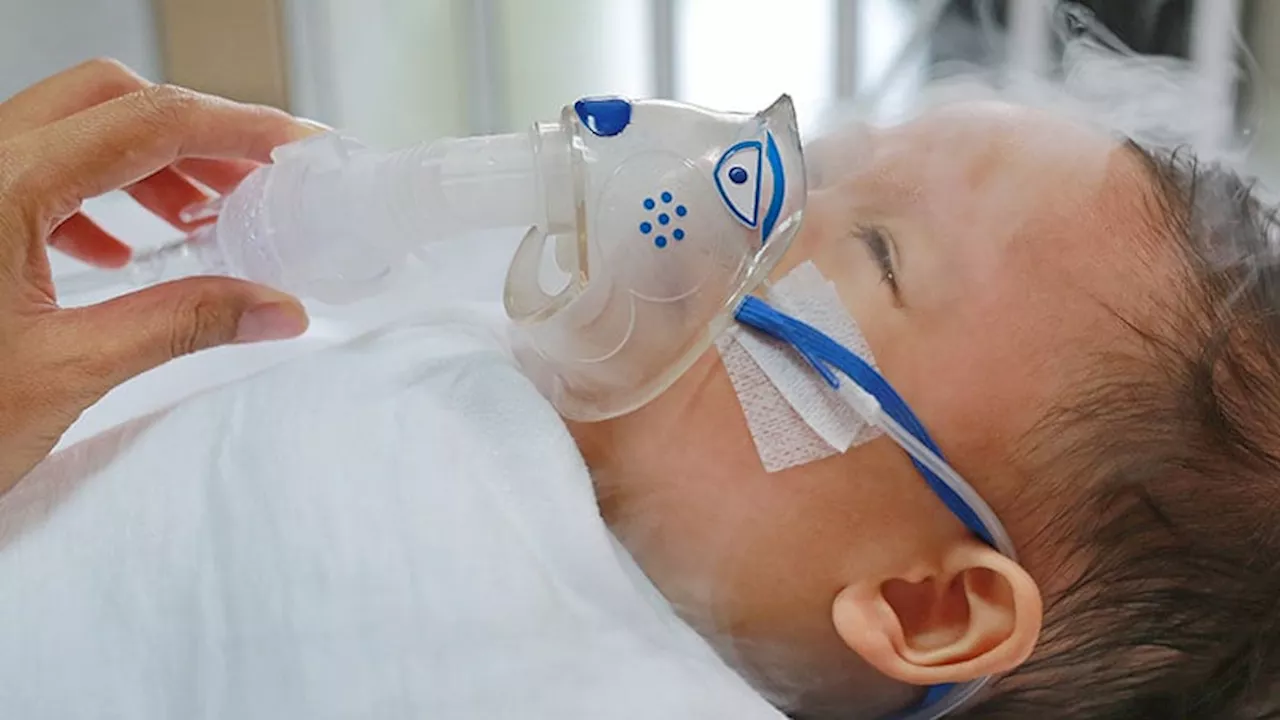
Widespread distribution of nirsevimab to infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection raised concerns about potential resistance mutations.
, an antibody targeting respiratory syncytial virus , is indicated for newborns and infants to prevent bronchiolitis. Available since September 2023, its widespread use may lead to resistance mutations. However, according to the French POLYRES study on prospective monitoring of nirsevimab, published recently in“The low prevalence of nirsevimab resistance mutations in treated patients is reassuring.
“This study is the largest surveillance study of nirsevimab virological failures to date. It was made possible thanks to collaborative synergy with the consortium of virologists at the ANRS MIE . It is a nationwide project that will help identify the resistance phenomenon associated with the widespread use of the drug.
The complete viral genome sequence was determined, specifically to identify mutations in the nirsevimab binding site . They also studied nirsevimab’s ability to inhibit viral replication in cell cultures .
RSV Infection Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection Pediatric Respiratory Infections Pediatric Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Pediatric RSV Infection Pediatric Cold
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Novel antibody platform tackles viral mutationsScientists have developed an innovative antibody platform aimed at tackling one of the greatest challenges in treating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2: their ability to mutate and evade existing vaccines and therapies.
Novel antibody platform tackles viral mutationsScientists have developed an innovative antibody platform aimed at tackling one of the greatest challenges in treating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2: their ability to mutate and evade existing vaccines and therapies.
Read more »
 Should First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade Be Used for NSCLC With Specific Mutations?Researchers conducted a subgroup analysis of POSEIDON trial data, then characterized underlying biologic mechanisms using mouse models.
Should First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade Be Used for NSCLC With Specific Mutations?Researchers conducted a subgroup analysis of POSEIDON trial data, then characterized underlying biologic mechanisms using mouse models.
Read more »
 A structurally informed human protein–protein interactome reveals proteome-wide perturbations caused by disease mutationsTo assist the translation of genetic findings to disease pathobiology and therapeutics discovery, we present an ensemble deep learning framework, termed PIONEER (Protein–protein InteractiOn iNtErfacE pRediction), that predicts protein-binding partner-specific interfaces for all known protein interactions in humans and seven other common model...
A structurally informed human protein–protein interactome reveals proteome-wide perturbations caused by disease mutationsTo assist the translation of genetic findings to disease pathobiology and therapeutics discovery, we present an ensemble deep learning framework, termed PIONEER (Protein–protein InteractiOn iNtErfacE pRediction), that predicts protein-binding partner-specific interfaces for all known protein interactions in humans and seven other common model...
Read more »
 Understanding how mutations affect diseasesThe human genetic code is fully mapped out, providing scientists with a blueprint of the DNA to identify genomic regions and their variations responsible for diseases.
Understanding how mutations affect diseasesThe human genetic code is fully mapped out, providing scientists with a blueprint of the DNA to identify genomic regions and their variations responsible for diseases.
Read more »
 New AI tool predicts protein-protein interaction mutations in hundreds of diseasesScientists have designed a publicly-available software and web database to break down barriers to identifying key protein-protein interactions to treat with medication. The computational tool is called PIONEER (Protein-protein InteractiOn iNtErfacE pRediction).
New AI tool predicts protein-protein interaction mutations in hundreds of diseasesScientists have designed a publicly-available software and web database to break down barriers to identifying key protein-protein interactions to treat with medication. The computational tool is called PIONEER (Protein-protein InteractiOn iNtErfacE pRediction).
Read more »
 New Drug Options Abound for Duchenne Muscular DystrophyMutations are a crucial factor, neurologist says, and steroids still play a role.
New Drug Options Abound for Duchenne Muscular DystrophyMutations are a crucial factor, neurologist says, and steroids still play a role.
Read more »