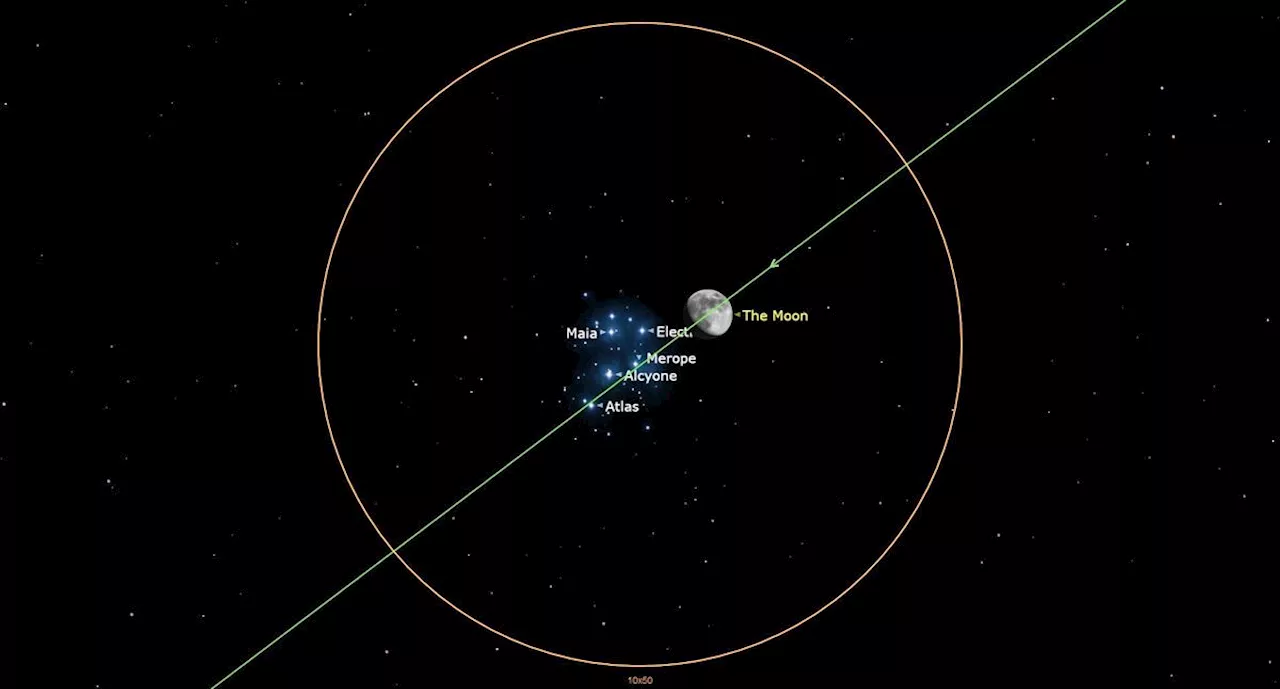
This January, skywatchers in North America will have a chance to observe a rare celestial event: the moon passing in front of the Pleiades star cluster.
Jam packed issues filled with the latest cutting-edge research, technology and theories delivered in an entertaining and visually stunning way, aiming to educate and inspire readers of all ages. An illustration of the sky on Jan. 9, 2025 showing the moon passing in front of the Pleiades star cluster.Whenever the moon shines near the Pleiades in December and January, it's nearly full. And on Thursday night, Jan. 9, the 10-day old moon will actually pass through the Pleiades .
Most North American observers will be able to watch as the moon passes in front of more than a few stars in this cluster (called an occultation) within a few hours, amid the dazzling lunar glare.will pass in front of that star as seen from various parts of our planet. Such a pattern is called a series and can last a few years or more.disappeared at the bright edge and reappeared from behind the dark edge of a waning gibbous moon. As far as the United States and Canada are concerned, the most favorable passages of the moon across the Pleiades during 2025 will come on Jan. 9, and again on Feb. 6 — specifically favoring the central and western US — and during the morning hours of July 20. There will be other opportunities in 2026 and 2027. The last series of occultations of the Pleiades took place between 2005 and 2010. Since this cluster lies 4 degrees north of the ecliptic — that great circle on the celestial sphere representing the sun's apparent path during the year — it can be occulted only when the ascending node of the moon's orbit is in the This situation repeats every 18.6 years, the time required for the ascending node to complete one circuit of the ecliptic. Hence a new'season' of Pleiades occultations began in September 2023 and will continue until July 2029. After 2029 the moon will pass south of the Pleiades until the next series commences in 2042.On Jan. 9, skywatchers can watch the dark limb of the 82%-illuminated waxing gibbous moon creep across this beloved star cluster, popularly known as the'Seven Sisters.' The details vary depending on your location, but out in the western U.S. and Canada the moon will already be among the Pleiades stars soon after the sun has set and the twilight sky darkens.The viewing circumstances markedly improve as you head farther to the east, where the sky will be decidedly darker; near and along the Atlantic Seaboard the moon will not start encroaching upon the cluster until at least a couple of hours after sunset.is preferable for viewing the fainter members of this star cluster disappear. Reappearances of stars will occur on the moon's bright limb, where the glare of the sunlit lunar landscape will likely hide the stars even in a telescope.Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!Receive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsors From New York City, observers can see the moon occult Electra (magnitude 3.7), Merope (4.2), and Alcyone at about 7:06 p.m., 7:35 p.m., and 8:18 p.m. EST, respectively. More than an hour later, the dark limb of the moon will reach the other side of the cluster and will cover Pleione (5.0) at 9:21 and Atlas (3.6) at 9:33. From New York, the moon will miss two of the seven brightest Pleiades stars, Maia (3.9) and Taygeta (4.3). Soon after 10 p.m. the moon will have moved beyond the cluster. On January 9th at 7 p.m. EST, as seen from New York City, the waxing gibbous moon will be very close to the Pleiades star cluster. Shortly thereafter, the moon will begin crossing in front of the Pleiades, taking about three hours to pass in front of this cluster. Note that the Pleiades appear about twice the size as the apparent diameter of the moon.Courtesy of the International Occultation Timers Association (IOTA), webpages are available that provide timetables for hundreds of locations for four stars in the cluster:Each page provides times for the disappearance and reappearance of the star in question. The times are given in Universal Time (UT) which is the same as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Since the occultation occurs after midnight UT, the calendar date is Jan. 10. When converting to your local time zone, the times will be before local midnight on the previous date (Jan. 9). As an example: For the star Atlas, as seen from Chicago, Illinois, this star will disappear at 1:53:25 UT on Jan. 10. Chicago is in the Central Time Zone and is six hours behind Universal Time. So, for the Windy City, Atlas will disappear at 7:53 p.m. CST on Jan. 9. Atlas is predicted to reappear at 2:51:59 UT, which corresponds to 8:51 p.m. CST. In addition to the timetable, a world map (Mercator projection) is provided, showing the region where the occultation will be visible. The boundaries are in different colors. The Cyan boundaries show the curves of the occultation disappearance or reappearance at moonrise or moonset. A continuous white line marks the nighttime northern and southern limits of the occultation. A continuous blue line denotes the occultation limits occurring during twilight, while a dotted red line depicts the occultation limits occurring in daylight. For Alcyone, the occultation takes place over much of the US and western Europe. For Atlas, visibility occurs over Canada, western Europe and most of the US, except for the Southeast states. For Electra and Maia, visibility will be confined to the southeast US, Central America, the Caribbean and west Africa.As reported here, this entire spectacle might not sound as arresting as it is in nature, but as a particular star creeps near the moon (in actuality, it is the moon that appears to be drifting eastward in relation to the stars) suddenly, as it reaches the unlighted and unseen part of our nearest neighbor in space, it disappears as though a switch were turned off. Or as Senior Editor of Sky & Telescope magazine, Alan MacRobert once noted:'Watching the moon cover or uncover bright stars gives a visceral sense of the moon's orbital motion. Try it!'to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: Joe Rao is Space.com's skywatching columnist, as well as a veteran meteorologist and eclipse chaser who also serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, the Farmers' Almanac and other publications. Joe is an 8-time Emmy-nominated meteorologist who served the Putnam Valley region of New York for over 21 years. You can find him on Twitter and YouTube tracking lunar and solar eclipses, meteor showers and more. To find out Joe's latest project, visit him on Twitter
Astronomy Moon Pleiades Occultation Stargazing
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Wolf Moon Rises: Everything You Need to Know About January's Full MoonWitness the stunning Wolf Moon, also known as the Old Moon, Ice Moon, or Snow Moon, as it graces the night sky in January 2025. Learn about its rising time, ideal viewing locations, and a special celestial event involving Mars.
Wolf Moon Rises: Everything You Need to Know About January's Full MoonWitness the stunning Wolf Moon, also known as the Old Moon, Ice Moon, or Snow Moon, as it graces the night sky in January 2025. Learn about its rising time, ideal viewing locations, and a special celestial event involving Mars.
Read more »
 Xbox Game Pass January Departures AnnouncedSix games are leaving Xbox Game Pass on January 16th, 2024. Subscribers get a 20% discount on these titles through the Microsoft Store. The article highlights and its potential for future collaborations.
Xbox Game Pass January Departures AnnouncedSix games are leaving Xbox Game Pass on January 16th, 2024. Subscribers get a 20% discount on these titles through the Microsoft Store. The article highlights and its potential for future collaborations.
Read more »
 Xbox Game Pass January Lineup Disappoints SubscribersXbox Game Pass's January lineup for the first half of the month has received a lukewarm reception from subscribers. The majority of additions are already available on the higher-tier Ultimate service, leaving little excitement for those who pay extra. While the service does see some new additions and improvements to its Quests system, the lackluster offerings are overshadowed by a number of games leaving the service next week.
Xbox Game Pass January Lineup Disappoints SubscribersXbox Game Pass's January lineup for the first half of the month has received a lukewarm reception from subscribers. The majority of additions are already available on the higher-tier Ultimate service, leaving little excitement for those who pay extra. While the service does see some new additions and improvements to its Quests system, the lackluster offerings are overshadowed by a number of games leaving the service next week.
Read more »
 Diablo IV Joins Xbox Game Pass in JanuaryDiablo IV is coming to Xbox Game Pass Ultimate and PC Game Pass in January. Along with the highly anticipated game, several other titles are joining the service, and some perks are available for Ultimate subscribers.
Diablo IV Joins Xbox Game Pass in JanuaryDiablo IV is coming to Xbox Game Pass Ultimate and PC Game Pass in January. Along with the highly anticipated game, several other titles are joining the service, and some perks are available for Ultimate subscribers.
Read more »
 Xbox Game Pass Adds Diablo and More in January 2025Xbox Game Pass subscribers will be treated to a new lineup of games in January 2025, including the classic Diablo for PC. The service will also see several games moving from Game Pass Ultimate to Game Pass Standard.
Xbox Game Pass Adds Diablo and More in January 2025Xbox Game Pass subscribers will be treated to a new lineup of games in January 2025, including the classic Diablo for PC. The service will also see several games moving from Game Pass Ultimate to Game Pass Standard.
Read more »
 Rare 'Black Moon' to Appear This WeekA 'Black Moon', the inverse of a 'Blue Moon', is an astronomical event that will occur this week. A 'Black Moon' is defined as the second new moon within a calendar month or the third new moon in a season with four new moons. This month's 'Black Moon' falls under the former category and will occur on Monday night.
Rare 'Black Moon' to Appear This WeekA 'Black Moon', the inverse of a 'Blue Moon', is an astronomical event that will occur this week. A 'Black Moon' is defined as the second new moon within a calendar month or the third new moon in a season with four new moons. This month's 'Black Moon' falls under the former category and will occur on Monday night.
Read more »