MIS-C in children: A distinct autoimmune response to COVID-19 unveiled MISC Research SARSCoV2 CrossReactivity SNX8Protein InflammatorySyndrome PostViral ImmuneResponse medrxivpreprint
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanJun 8 2023Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. In a recent study posted to the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers examine a large dataset of patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children to determine whether their autoantibodies target a different set of host proteins as compared to healthier controls.
Background Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection can lead to long-term dysregulation of the immune system and a broad spectrum of secondary infections and diseases, including post-acute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 in adults. In children, while the outcomes of COVID-19 are generally mild, rare cases progress to MIS-C.
About the study In the present study, researchers used cohorts of children with a history of COVID-19 with and without MIS-C to profile the autoreactive antibodies and antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2 using phage immunoprecipitation and sequencing , which has been extensively used in various diseases to identify novel autoantigens.
Logistic regression machine learning was used to identify the presence of differentially enriched peptides that distinguish MIS-C samples from at-risk control samples. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to identify statistically enriched autoreactivity. The validity of the findings was confirmed using an independent cohort comprising MIS-C patients and children severely affected by acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Study findings The antibody response in MIS-C patients was differentially reactive to SNX8 and a specific domain of the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 as compared to the antibody response of the at-risk controls. Furthermore, the SNX8 protein and this viral nucleocapsid region had remarkable biochemical similarities.
The SNX8 protein is functionally linked to the mitochondrial antiviral signaling pathway, and MIS-C is thought to be associated with an increased autoimmune response by SNX8 against tissues with high MAVS pathway expression. The researchers believe these results indicate similarities with other diseases, such as paraneoplastic autoimmune disease, where exposure to a novel antigen results in autoimmunity.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Prenatal COVID boosts protective power of breast milkPrenatal COVID boosts protective power of breast milk BreastMilk ExtracellularVesicles SARSCoV MaternalHealth InfantDevelopment COVID MultiOmics MetabolicReprogramming MucosalTissue ImmuneModulation PostCOVID biorxivpreprint
Prenatal COVID boosts protective power of breast milkPrenatal COVID boosts protective power of breast milk BreastMilk ExtracellularVesicles SARSCoV MaternalHealth InfantDevelopment COVID MultiOmics MetabolicReprogramming MucosalTissue ImmuneModulation PostCOVID biorxivpreprint
Read more »
 Study: Using a diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 reduces risk of developing long COVID by 40%Taking a two-week course of metformin, a safe and affordable diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 leads to 40% fewer long COVID diagnoses over the following 10 months, compared to individuals taking a placebo, finds a new study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal.
Study: Using a diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 reduces risk of developing long COVID by 40%Taking a two-week course of metformin, a safe and affordable diabetes medication after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 leads to 40% fewer long COVID diagnoses over the following 10 months, compared to individuals taking a placebo, finds a new study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal.
Read more »
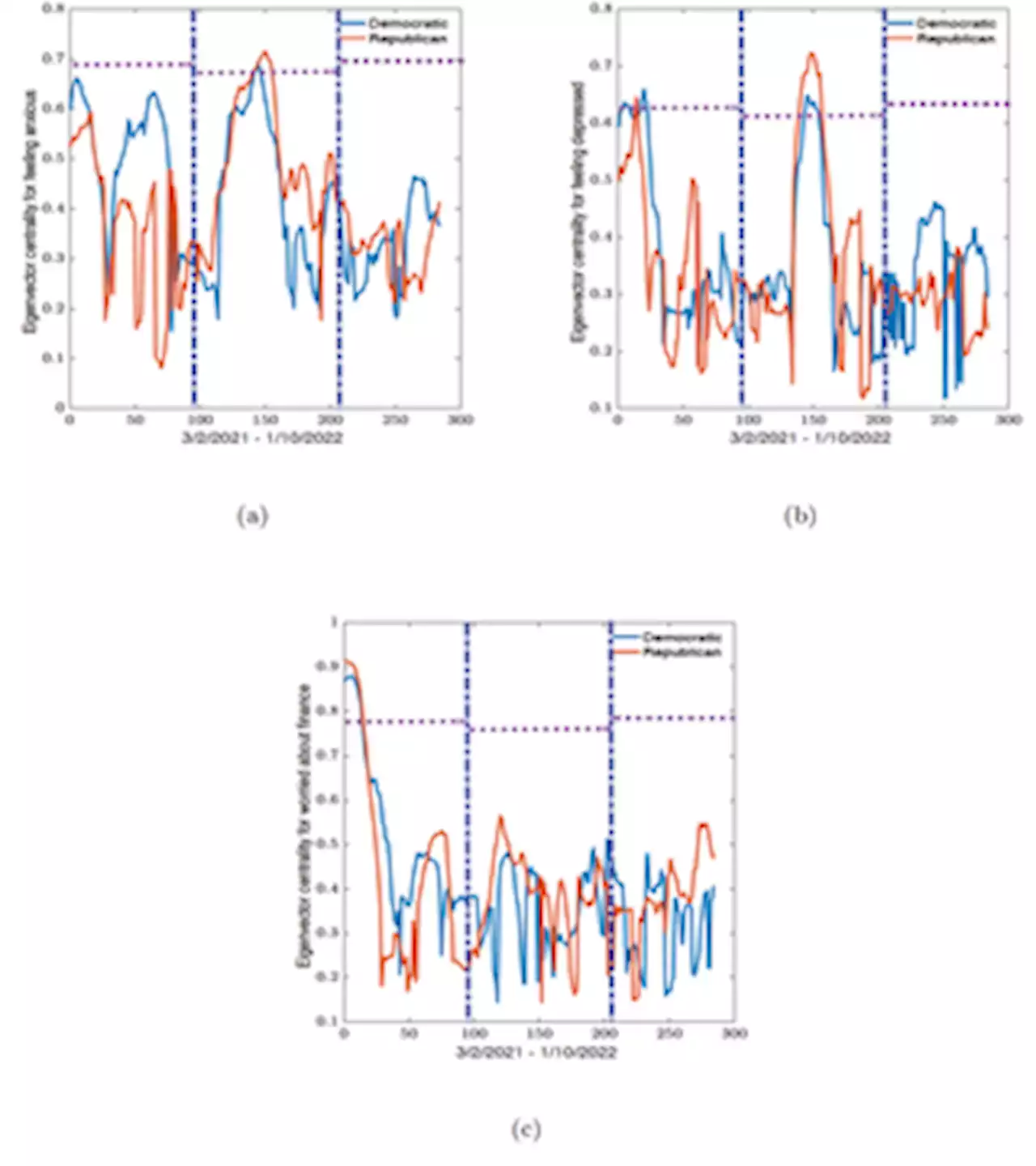 Understanding mental health trends during COVID-19 pandemic in the United States using network analysisThe emergence of COVID-19 in the United States resulted in a series of federal and state-level lock-downs and COVID-19 related health mandates to manage the spread of the virus. These policies may negatively impact the mental health state of the population. This study focused on the trends in mental health indicators following the COVID-19 pandemic amongst four United States geographical regions, and political party preferences. Indicators of interest included feeling anxious, feeling depressed, and worried about finances. Survey data from the Delphi Group at Carnegie Mellon University were analyzed using clustering algorithms and dynamic connectome obtained from sliding window analysis. Connectome refers to the description of connectivity on a network. United States maps were generated to observe spatial trends and identify communities with similar mental health and COVID-19 trends. Between March 3rd, 2021, and January 10th, 2022, states in the southern geographic region showed similar trends for reported values of feeling anxious and worried about finances. There were no identifiable communities resembling geographical regions or political party preference for the feeling depressed indicator. We observed a high degree of correlation among southern states as well as within Republican states, where the highest correlation values from the dynamic connectome for feeling anxious and feeling depressed variables seemingly overlapped with an increase in COVID-19 related cases, deaths, hospitalizations, and rapid spread of the COVID-19 Delta variant.
Understanding mental health trends during COVID-19 pandemic in the United States using network analysisThe emergence of COVID-19 in the United States resulted in a series of federal and state-level lock-downs and COVID-19 related health mandates to manage the spread of the virus. These policies may negatively impact the mental health state of the population. This study focused on the trends in mental health indicators following the COVID-19 pandemic amongst four United States geographical regions, and political party preferences. Indicators of interest included feeling anxious, feeling depressed, and worried about finances. Survey data from the Delphi Group at Carnegie Mellon University were analyzed using clustering algorithms and dynamic connectome obtained from sliding window analysis. Connectome refers to the description of connectivity on a network. United States maps were generated to observe spatial trends and identify communities with similar mental health and COVID-19 trends. Between March 3rd, 2021, and January 10th, 2022, states in the southern geographic region showed similar trends for reported values of feeling anxious and worried about finances. There were no identifiable communities resembling geographical regions or political party preference for the feeling depressed indicator. We observed a high degree of correlation among southern states as well as within Republican states, where the highest correlation values from the dynamic connectome for feeling anxious and feeling depressed variables seemingly overlapped with an increase in COVID-19 related cases, deaths, hospitalizations, and rapid spread of the COVID-19 Delta variant.
Read more »
 Is discontinuing universal SARS-CoV-2 testing at hospital admission in England and Scotland associated with increased hospital-onset infections?Is discontinuing universal SARS-CoV-2 testing at hospital admission in England and Scotland associated with increased hospital-onset infections? JAMAInternalMed harvardmed DeptPopMed SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid infection
Is discontinuing universal SARS-CoV-2 testing at hospital admission in England and Scotland associated with increased hospital-onset infections?Is discontinuing universal SARS-CoV-2 testing at hospital admission in England and Scotland associated with increased hospital-onset infections? JAMAInternalMed harvardmed DeptPopMed SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid infection
Read more »
 Covid-19 pandemic 'lowered cancer survival rates' in NIThe Covid pandemic had an adverse effect on how cancer patients were treated, according to the Northern Ireland Cancer Registry
Covid-19 pandemic 'lowered cancer survival rates' in NIThe Covid pandemic had an adverse effect on how cancer patients were treated, according to the Northern Ireland Cancer Registry
Read more »
 Rishi Sunak’s Covid inquiry secrecy will destroy the last shred of trust in the ToriesNo-nonsense chair Lady Hallett is determined to defy those who say the inquiry is a waste of time and money
Rishi Sunak’s Covid inquiry secrecy will destroy the last shred of trust in the ToriesNo-nonsense chair Lady Hallett is determined to defy those who say the inquiry is a waste of time and money
Read more »